Choose Smarter Spend Management Today!
Finance teams spend hours reconciling mismatched invoices between their P2P and O2C systems, with higher stakes than ever. Processing a wrong vendor invoice now carries a penalty of ₹25,000 under new compliance regulations in India.
The confusion stems from these processes being mirror images of each other: P2P handles vendor payments, while O2C manages customer collections. Yet many treat them as separate islands.
This disconnect creates data silos, delayed payments, and frustrated customers waiting for order fulfilment. Having clarity on how P2P and O2C processes intersect can eliminate these costly bottlenecks for businesses and create a seamless financial workflow.
Key Takeaways
P2P controls spend and vendor management; O2C drives order fulfilment and revenue collection.
Automation removes manual work and reduces costly errors across both processes.
Integrating P2P and O2C prevents data silos and eases reconciliation.
With tighter compliance rules, even small invoice errors can lead to hefty penalties; accurate systems are essential.
High-performing companies connect P2P and O2C into a single financial workflow, not separate silos.
What is Procure to Pay (P2P)?

Procure-to-pay (P2P) is an organisation's end-to-end procurement lifecycle that transforms purchasing decisions into vendor payments while maintaining financial controls and compliance standards.
In other words, P2P represents the critical bridge between operational needs and cash outflow management. A well-designed P2P system enforces budgetary control, captures GST and TDS obligations accurately, and eliminates manual handoffs.
At scale, P2P plays a strategic role in providing real-time spend visibility and maintaining compliance with internal procurement policies and external regulatory frameworks.
The process involves multiple touchpoints: purchase requisitions, vendor onboarding, contract negotiations, goods receipt verification, and invoice processing. Each step requires careful documentation to ensure a smooth workflow.
The typical Procure to Pay process cycle involves:
Identifying the Need: A department realises it needs a specific product or service.
Selecting a Vendor: The company chooses a supplier that can provide the required goods or services.
Creating a Purchase Order involves submitting a formal request to the vendor for the product or service.
Receiving goods/services: The company gets the product or completes the service.
Invoice Processing: The next step involves checking the vendor's invoice against the purchase order and delivery receipt.
Vendor Payment: After verifying the invoice, payment is made to the vendor.
For example, imagine a business needs new laptops. The IT department selects a vendor, places an order, receives the laptops, verifies the invoice, and then processes the payment.
Several companies struggle with P2P because it involves external parties beyond their control. Vendors might delay shipments, send incorrect invoices, or change pricing without notice. These variables make P2P inherently complex and prone to errors.
While P2P governs how companies manage their outbound cash flow, it’s only one half of the financial operations.
To get a complete picture of operational efficiency, evaluating how money flows into the business is equally important. That brings us to the other half of the financial operations—order-to-cash (O2C).
What is Order to Cash (O2C)?
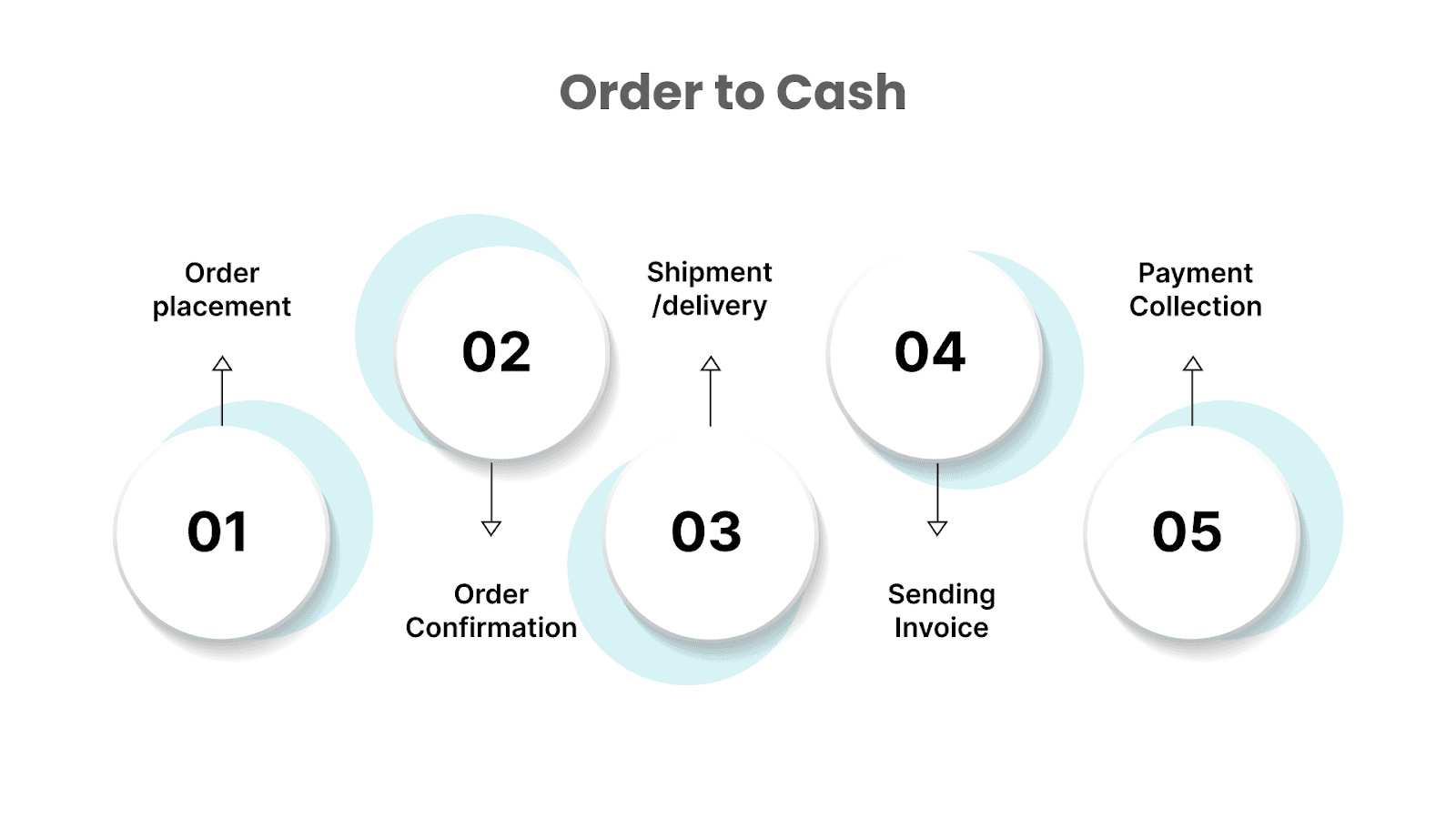
Order-to-cash (O2C) is the process a company follows when selling products or services. It starts when the customer places an order and ends when the company receives payment. Basically, the term refers to the whole order fulfilment cycle.
While it may sound straightforward on paper, every stage in between, right from order confirmation to follow-up, can directly impact customer satisfaction and cash flow.
Here’s a closer look at how this process typically unfolds in most organisations:
Order placement: A customer places an order for a product or service.
Order Confirmation: The company confirms the order details, including price and delivery date.
Shipment/delivery: The product is delivered to the customer, or the service is provided.
Invoicing: A bill is sent to the customer for payment.
Payment Collection: The customer pays for the product or service they receive.
Consider an online electronics store: when someone orders a smartphone, O2C manages the entire journey from processing their order to receiving their payment and updating inventory records.
O2C processes are owned internally. This means finance teams can fine-tune metrics like cash conversion cycle, reduce revenue leakage, and improve audit readiness without relying on external inputs.
Since both P2P and O2C involve invoices, payments, and approvals, it's easy to confuse the two. The confusion further deepens when vendors become customers or when your company provides services while also purchasing from suppliers.
Adding multiple departments that handle different parts of each process can lead to a recipe for operational chaos.
To help you navigate this complexity and simplify things, we have highlighted the key differences and explained how understanding them can improve your overall business efficiency.
Order-to-Cash vs. Procure-to-Pay: Key Differences
P2P and O2C might look like two ends of the same transaction cycle, but operationally, they’re driven by different stakeholders, risks, and financial outcomes.
Misunderstanding their friction points, e.g., external vendor dependencies in P2P vs. internal credit controls in O2C, leads to poor cash visibility and audit exposure.
In businesses where entities double as both vendors and customers, the boundary blurs even further, compounding errors in reconciliation and reporting.
To help you untangle this complexity, the table below outlines the core operational differences between P2P and O2C:
Aspect | Procure-to-Pay (P2P) | Order-to-Cash (O2C) |
Primary Focus | Spending money on goods/services. | Generating revenue from sales. |
Direction | Outbound cash flow. | Inbound cash flow. |
Key Stakeholders | Procurement, AP, vendors. | Sales, AR, customers. |
Risk Factor | Vendor fraud, overpayment. | Customer default, bad debt. |
Compliance | Vendor onboarding, tax regulations. | Revenue recognition, customer credit. |
Performance Metrics | Cost savings, payment accuracy. | Revenue growth, collection efficiency. |
Document Flow | PO → Goods Receipt → Invoice → Payment. | Sales Order → Delivery → Invoice → Payment. |
Control Level | Limited (depends on vendors). | High (internal processes). |
Financial Impact | Directly impacts cash flow and working capital. | Affects costs, budgets, and vendor relationships. |
Main Bottlenecks | Invoice matching, approval delays. | Credit checks, payment collection. |
These processes are interconnected but serve distinct purposes. Having complete clarity on their differences can help you manage both processes more effectively and avoid silly errors.
As your business grows, managing both processes manually can become exceedingly difficult. This is where automation bridges the gap and eliminates manual handoffs.
How Automation Transforms P2P and O2C Operations
Nearly every finance team has jumped on the automation bandwagon, with 98% reporting investments in digital transformation initiatives. Meanwhile, companies that optimise their financial processes through automation consistently slash processing time by 30-40%.
So, if you haven't automated yet, you're simply missing out on opportunities to accomplish significantly more without exhausting your team or burning through overtime budgets.
Advantages of Automating P2P Process
The procurement software industry tells an interesting story about market confidence. Current market valuation stands at ₹48,000 crore, with projections reaching around ₹1.1 lakh crore by 2031.
This explosive growth reflects how seriously companies take P2P automation benefits, which include:
Eliminates Invoice Errors: Automated matching prevents critical invoice errors by cross-referencing purchase orders with receipts and invoices before processing payments.
Improved Accuracy: Automation minimises human error in tasks like invoice processing, order creation, and vendor payments. With P2P automation platforms like Kodo, there's less room for mistakes. Kodo helps ensure that orders and payments are processed correctly the first time, which saves both time and money.
Speeds Up Approval Workflows: Digital routing sends documents to the correct approvers instantly, cutting approval cycles from weeks to days through automated notifications and escalations.
Reduces Vendor Payment Delays: Real-time tracking shows exactly where invoices sit in the process, helping you avoid late payment fees and maintain strong supplier relationships.
Improves Compliance Tracking: Built-in audit trails capture every transaction detail automatically, making regulatory reporting effortless during tax season or compliance reviews.
Cuts Processing Costs: Automated data entry and validation eliminate manual work, reducing per-invoice processing costs while improving accuracy rates.
Advantages of Automating the O2C Process
Similarly, O2C automation delivers measurable improvements across your entire revenue cycle. Here's why smart companies prioritise O2C digital transformation over manual processes.
Accelerates Order Processing: Automated order validation and inventory checks process customer requests within minutes, reducing order-to-shipment time and improving customer satisfaction scores significantly.
Minimises Collection Delays: Smart reminders and payment tracking automatically follow up with customers, reducing the number of days sales outstanding and improving cash flow predictability for better planning.
Eliminates Billing Mistakes: Automated invoice generation pulls accurate data directly from order systems, preventing pricing errors and disputes that typically delay customer payments.
Enhances Credit Management: Real-time credit scoring and limit monitoring prevent bad debt situations by flagging risky customers before orders ship or credit limits exceed.
Standardises Revenue Recognition: Automated accounting entries ensure accurate revenue booking in accordance with accounting standards, simplifying month-end close and financial reporting requirements for auditors.
The benefits we just discussed paint an exciting picture of automated P2P and O2C processes. However, the implementation reality often differs from vendor promises and demo presentations. Even companies with solid automation strategies encounter obstacles that can derail timelines and budgets.
Challenges of Implementing Automation in O2C and P2P
The promise of seamless automation often crashes into reality during the implementation phase. While the benefits are clear, the path to achieving them requires navigating technical complexities, employee resistance, and budget constraints.
Smart planning helps, but some challenges are simply part of the transformation journey.
High Initial Investment Costs: Quality automation platforms require significant upfront expenditures on software licenses, implementation services, and system integration work, which can strain budgets before delivering returns.
Employee Resistance and Training: Teams fear job displacement and struggle with new workflows, requiring extensive change management efforts and comprehensive training programmes to ensure successful user adoption.
Data Migration Complexities: Moving years of financial data from legacy systems into new platforms creates risks of data loss, formatting issues, and temporary operational disruptions.
Integration with Existing Systems: Connecting automation tools with current ERP, CRM, and accounting software often reveals compatibility issues that demand custom development work and extended timelines.
You need the right automation software to turn these challenges into competitive advantages and unlock the full potential of your financial processes.
How Kodo Can Help With Procure-to-Pay Management
Kodo offers next-generation spend management solutions, helping businesses transform their procure-to-pay processes from manual chaos to automated efficiency.
Our comprehensive suite serves 2000+ companies, including Urban Platter and Dharma Productions, delivering measurable results across diverse industries.
Purchase Request: Create and submit purchase requests with built-in approval workflows that maintain transparency and control from day one of every procurement cycle.
Purchase Order Automation: Generate professional POs instantly after approval, deliver them directly to suppliers, and maintain searchable digital archives of all purchasing documentation automatically.
Invoice Management: Capture invoices through email, uploads, or supplier portals, automatically matching them to purchase orders and routing them for approval before integration into the accounting system.
Vendor Payments: Simplify vendor payments through our centralised bank transfer platform that processes efficient transactions tailored to your specific business requirements and payment schedules.
Versatile Integration: Connect directly with major systems like Zoho, Tally, Oracle, and SAP to synchronise financial data and eliminate duplicate entries across your existing technology stack.
Ready to see how Kodo can transform your procurement process? Book a demo today and discover why leading companies choose Kodo.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between P2P and O2C helps you build stronger financial processes that support business growth. Automation eliminates manual bottlenecks, reduces costly errors, and frees your team to focus on strategic initiatives.
However, successful implementation requires careful planning, proper training, and choosing the right technology partner for long-term success.
Kodo breaks down complex procurement challenges into easily manageable workflows that save time, reduce costs, and improve vendor relationships.
Our platform handles everything from purchase requests to final payments, giving you complete visibility and control over your spend management process.

Book a strategy call today to discover how Kodo can revolutionise your P2P operations.
FAQs
How does automation improve P2P and O2C processes in finance?
Automation reduces manual errors, speeds up approvals, ensures compliance, and improves real-time visibility across both procurement and revenue cycles.
Why is it important to integrate P2P and O2C workflows?
Integration eliminates data silos, prevents invoice mismatches, improves cash flow forecasting, and streamlines financial reporting across both processes.
What are the common challenges in P2P and O2C process mapping?
Misaligned master data, manual handoffs, fragmented systems, and unclear ownership often lead to delays, mismatches, and compliance gaps.
Which KPIs should CFOs track for P2P and O2C performance?
For P2P: payment accuracy, cost per invoice, and vendor cycle time.
For O2C: DSO (days sales outstanding), collection efficiency, and billing error rates.
What are P2P, R2R, and O2C in finance operations?
P2P (Procure-to-Pay), R2R (Record-to-Report), and O2C (Order-to-Cash) are three core finance process cycles:
P2P manages how a company purchases goods/services and pays vendors.
O2C handles customer orders, invoicing, and payment collection.
R2R involves consolidating financial data, closing books, and generating reports for compliance and analysis.
Together, these cycles form the backbone of end-to-end finance operations in any enterprise.